If you’re considering getting into the commercial real estate market, it’s a good idea to get familiarized with CMBSs. This post will give you a better understanding of what they are and how they can help you.
Commercial mortgage-backed securities, or CMBS as they are popularly called, are fixed income securities with an underlying commercial real estate as a mortgage for the payment of coupons and principal invested. Unlike the traditional mortgage-backed securities, which have residential real estate as underlying mortgages, CMBS have commercial properties as the mortgage.
Purpose
The major purpose of CMBS, like MBS, is to provide liquidity options to commercial lenders. They allow the lenders to reduce the risk of their financing by allowing them to create derivatives of the loans into financial instruments and sell them out in the commercial market as investment opportunities. Meanwhile, it also gives investors the ability and risk appetite to invest in these instruments and generate regular cash flows through coupon payments. Retail investors can invest in these instruments through third-party products such as mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that specialize in investing in such products. Direct investments in such products are limited to ultra-high net worth individuals and family offices due to the large ticket size in these products.
Structure
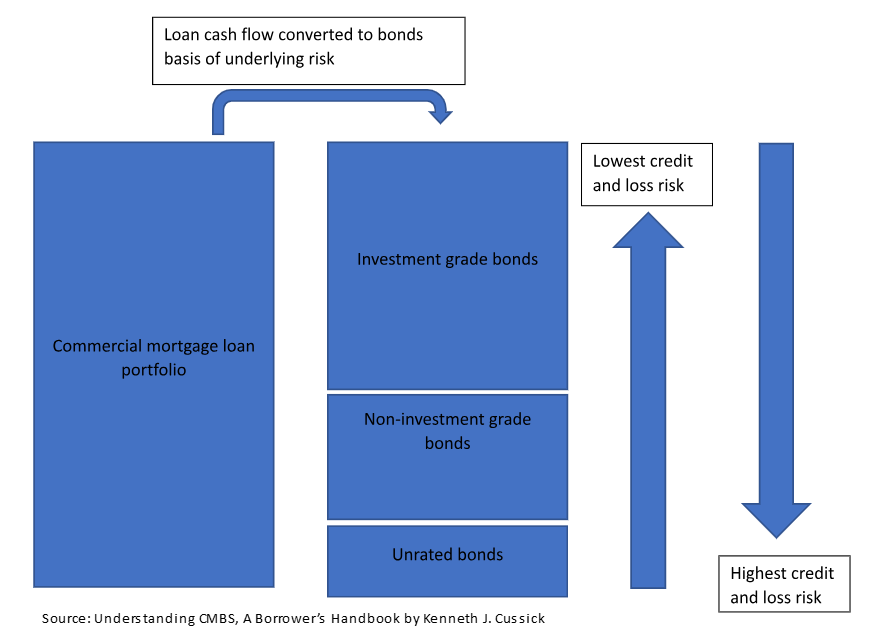
The structure of CMBS works on the pooling of loans given by lenders for commercial properties. These loans are pooled together on the basis of their cash flow to create fixed-income securities that they can sell to investors. The securities are divided into multiple layers basis the risk that they carry in terms of credit and loss. The major classification of these securities include:
Investment grade bonds – These are securities that carry lower risk in terms of credit and loss and thus have better credit ratings such as AAA, AA, and other higher ratings from credit rating agencies. These are considered safer investment opportunities for investors.
Non-investment grade bonds – These are pooled commercial loan accounts that carry a higher risk of credit and loss compared with investment graded and thus are lower by credit rating agencies such as BB, B, etc. Since these carry higher risk, they are suitable for investors with a risk appetite. They will, however, have a higher coupon to compensate for the larger risk.
Unrated bonds – These bonds carry the highest risk in terms of credit and loss probability and thus are unrated by credit risk due to this potent danger. Investors only with the highest risk appetite and ability to bear the loss should invest in such bonds.
Diagrammatic representation of CMBS
Benefits
CMBS have multiple benefits across the value chain for borrowers, lenders and investors.
Borrowers – Since the borrower is mortgaging their property for the loan, they can procure a lower interest on the monies. Further, they can also generate a higher value of loan basis the valuation of the underlying property. Further, in many cases, the upfront fees are also lower than traditional loans lowering the overall cost to the borrower.
Lenders – The most significant benefit to the lender is that they can securitize the loan portfolio, thus improving the overall cash flow in their financial portfolio. They can also enhance their loan portfolio, thus improving their overall balance sheet size and revenue opportunities.
Investors – It provides investors with an opportunity to invest in a fixed income portfolio of securities basis their risk-return appetite considering the wide type of bond tranches available in this segment.
Drawbacks
While CMBS loans are a suitable conduit for all parties in the CMBS ecosystem, there are also some drawbacks to these securities.
High valuation – Since these bonds are pooled loan accounts, these are of high value, which is beyond the reach of individual investors who want to take exposure to these securities. Only ultra-high net worth individuals or family offices tend to have the monies to directly invest in these securities, limiting the investment opportunities for investors. Investors need to route their investments through ETFs or mutual funds that invest in these securities.
Complex – These CMBS loans have a complex structure compared with traditional loans since they need to be collateralized before they are securitized. Further, since the underlying securities are commercial properties, the valuation is relatively complicated compared with residential properties. Because of the complexity of the products, these instruments require multiple participants in the value chain, which includes various types of servicers, trustees, custodians and credit rating agencies, to finally be put up these instruments in the market for investment purposes.
Summing up
CMBS are an excellent conduit to convert commercial lending into collateralized fixed income securities for investment purposes. However, unlike traditional mortgage-backed securities (MBS), CMBS loans are mortgaged on commercial properties and thus are more complex than the former. Investors should look at the underlying tranche of CMBS, such as investment grade, non-investment grade and unrated bonds, to identify the risk of credit and loss before making any investment decision basis their risk-return profile. Individual investors can route their investments in these instruments through mutual funds or ETFs that invest in such securities. In contrast, ultra-high net worth individuals and family offices can afford to invest directly in these instruments.




